Embracing AI in Education: Key Insights from UNESCO Digital Week 2024
In a world where 4th graders have already been navigating social media and engaging with various AI applications, the conversation around technology in education has never been more urgent. As we are now utilize technologies that were once seemed fiction in the past, it becomes imperative to recognize that not all tech is created equal; some serve merely as gimmicks while others hold the potential to profoundly impact learning. The recent UNESCO Digital Week 2024, hosted in Paris,France, highlighted the digitalization especially Generative AI integration with education presenting an opportunity to all policy makers, educators and related parties to examine how we can harness AI as a catalyst for change in educational settings. The 4 day event has attracted teachers, educators, stakeholders and policy makers internationally to this table to discuss on their own experience on issues around AI application and framework for education.Digital Learning Week Opening Speech
Regional and National Strategies
The integration of AI in education varies significantly across regions, with each country developing tailored strategies.
Finland stands out for its emphasis on bilateral collaboration, viewing AI competency as a collective responsibility rather than a national endeavor. The Finnish approach is deeply rooted in a strong commitment to research and development, with 4% of its GDP allocated to education.
Brazil focuses on equity in AI access, promoting online teacher training platforms to equip educators with necessary skills, ensuring that all students can benefit from these advancements.
Armenia:launched FAST system: stem education as a national criteria for High school level;Scalable and sustainable model : through public and private collaborationStrategize geographically;movable internet zoom
France :Sarah: AI powered assistant for high school : math , essaysGhana: integrate in basic education 4-6 ; coding;Strategy: teacher training center in middle schools;framework works;learns from other countries and duplicate experience; training among teachers;
OECD : teacher not only implementation of curriculum but also design of that; changing complexity of dynamic for current generation to handle——digital literacy ;Get students prepared for Ethical challenge of AI age
Afica Union:youngest continent with prominent of workforce in developing AI labour ;Youngest continent;70% Africa under 30s old ; African students saving up for subscription for GPT4Build Africa’s future :from AI literacy to leadership ; regulation needs to happen nowYoung teachers’ future pedagogy change: share, lead, mentor; catalyst for change,enabler for innovation;Open educational resources;15 millions teachers, AI come to make up the gap; provide share the knowledge;Intersection with education : school curriculum content; media and information literacy
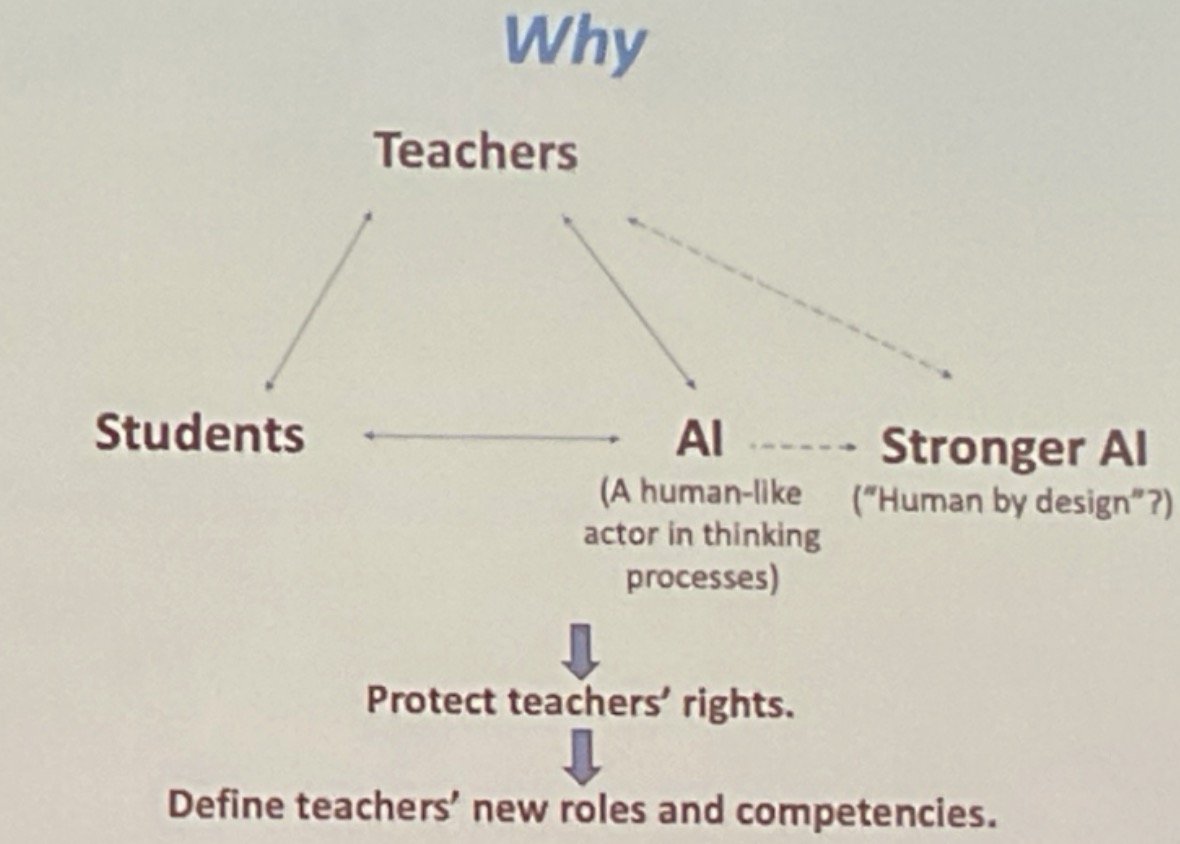
UNESCO’s New AI Framework
During the event, UNESCO introduced a new AI framework aimed at providing guidance for both students and teachers. This framework prioritizes ethical AI usage, fostering critical thinking, and ensuring digital inclusivity. By promoting AI competencies, UNESCO seeks to empower learners to navigate the complexities of an increasingly digital world, equipping them with the skills necessary to face future challenges. Access to the document here:(https://www.unesco.org/en/articles/ai-competency-framework-teachers)
UNESCO’s position of AI competency: AI to promote green digital citizens;AI is a tech
to help understand climate change
to drive greening curriculum through learning experience
power green energy sustainability and innovation
collaborate 21st green digital global citizens
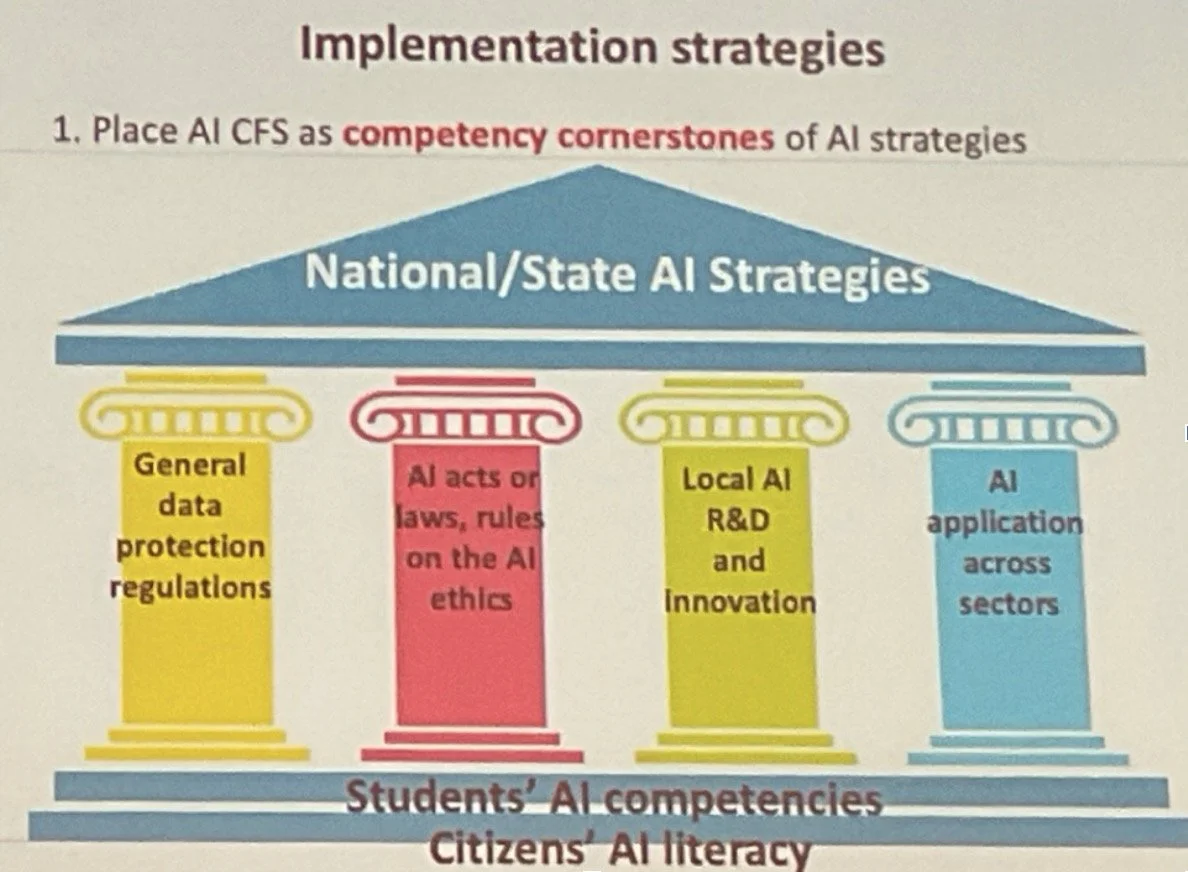
Unesco launched 2024 AI Framework for teachers and students
AI framework for global usage
Global AI Applications by Companies and Startups
Basically, most of the AI application so far are all designed for teachers’s use first.
Children must access to it under the guidance of teachers. The most important ability in consensus is the selection of dataset.
Linguistic correction is the most popular function among all kinds of applications.
Innovative AI applications were highlighted by various companies and startups worldwide. For example, Mistral AI, based in France, focuses on developing text-based generative AI models that support language learning and cultural representation.Meanwhile, Valetika offers an ethics teaching tool that generates engaging lesson plans for primary and secondary education, promoting critical engagement with AI in the classroom. These applications demonstrate how AI can be a catalyst for change and an enabler for innovation, encouraging students to be creators rather than passive consumers in their learning processes.Fobizz, AI grading courses selection product with 300 courses in German; it is for pregrading toolRaspberry Pi/ExperienceAI.org: 1)Research informed: resources are collaboration between learning and research teams at RPF 2)Collaboration with Google DeepMind industry leader in the fleld 3) Emphasize on addressing diversity and under representedTeach AI , US : Leading while learning: Practical examples of guidance and policies for local and national education systems; TeachAl is an initiative that guides education leaders and policymakers in transforming education through teaching with Aland teaching about Al. Valetika, Malta: VALETIKA is a versatile Ethics teaching tool for primary and secondary education It generates lesson plans with engaging activities, videos and presentations based on the national ethics syllabus, while also analyzing and offering feedback on students' reflective journals based on a specific rubric Teacher training organized by the Ministry for Education is also made available to Ethics teachers in Private Schools;
University Research on AI in Education
University research is playing a pivotal role in understanding and advancing AI in education. Institutions like the University of Sydney , MIT, Harvard, Oxford and Georgia Tech are exploring the impact of generative AI on self-directed learning and educational outcomes. Projects such as Cogniti aim to transform feedback mechanisms in higher education, while Georgia Tech's Jill Watson project enhances adult learning through AI.
University of Sydney, Australia
Project: Cogniti: Transforming feedback and learning in higher education
Professor: Mr Danny Liu, Professor, University of Sydney, Australia
GeorgiaTech
Project name: Jill Watson
Research Scientist:MS Pratyusha Maiti;
Theme: Enhancing self-directed adult learning with generative AI: Exploring Jill Watson’s impact
Oxford:
Owner: Cindy Ong: researcher, from Uni of Oxford;
Subject : Digitized Reading’s effect for 3-9 years old longitudinal research;learning on child users;
method: interview with children
Parameter:
Habits of tech use;
perception of learning ;
patterns or questions about: playing game; hating stem, problem solving;give up when too difficult and shift to other games allow to start again;
Outcome:
games: Shaping values what to learn
worth thinking: what is value in perception at all, should think first when design the game;
Game is not just a game; learning faster about culture in disguise of games and videos ;
Gamification does have influence whether or not it is designed that way;
perfect safe product does not exist, find the middle place;
Tasks and Challenges:
Bring different stakeholders to table
Fundraising: research needs more time to testify itself
Product manager experience
Next step to research on:
What is acceptable language for 3 year old;
Ethical design development is important;
How to shape children ‘s habit when using AI
Models of behavior analysis in front of AI;
MIT:
Projectname : Democratizing data science and Al literacy through student-centered interdisciplinary curricula
Phd student: Ms Prena Ravi, PhD Candidate, MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (SAIL), Massachusetts Institute of Technology, United States of America
Mr John Masla, Assessment Specialist, Scheller Teacher Education Program (STEP) Lab, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, United States of America
The speed of AI development is outpacing traditional educational reforms, making it essential for existing infrastructures to be adaptable, rather than merely translated into new contexts.
Conclusion
The insights gathered from UNESCO Digital Week 2024 underscore the transformative potential of AI in education. As countries and organizations continue to explore innovative strategies for integration, a strong emphasis on collaboration, ethical considerations, and ongoing research will be vital in shaping a future where technology supports and enhances human learning. Through these efforts, we can foster a generation of learners equipped to thrive in an increasingly complex digital world.